HVOF Tungsten Carbide Coating Properties, Structure And Applications
WC-Co tungsten carbide coatings are probably the second most widely used wear resistant coatings after WC-10Co-4Cr.
Kermetico HVAF and HVOF tungsten carbide coatings have excellent resistance to sliding wear, abrasion and erosion despite lower corrosion resistance than WCCoCr.
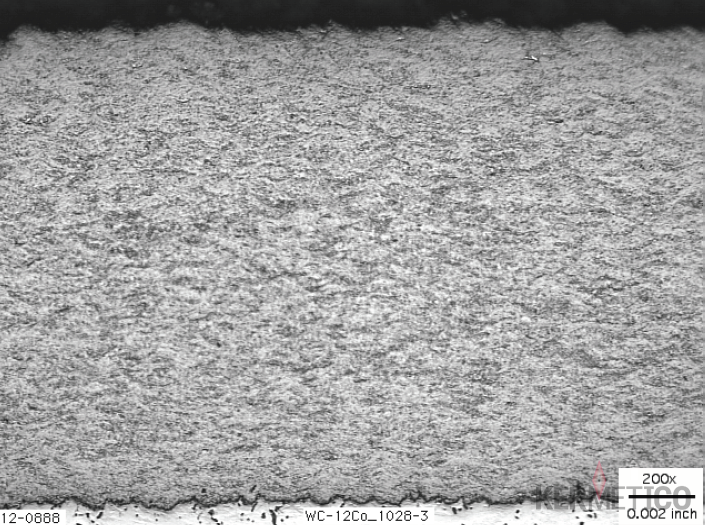
The Kermetico HVAF WCCo coatings are gas-tight (non-permeable to gas and liquid) at 50 microns | 2 mils.
Tungsten Carbide WC-Co 88/12 Feedstock Properties
HVAF and HVOF Tungsten carbide coatings are sprayed with WC-Co agglomerated and sintered powder
| Nominal composition | wt.% |
|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | base |
| Total carbon | 5.3-5.4 |
| Cobalt | 11-13 |
Powders are available where cobalt is replaced with nickel.
The Properties Of HVAF WC-Co Tungsten Carbide Coatings On Steel
WC-12Co thermal spray coatings are usually harder compared to coatings of WC-17Co as a result of higher tungsten carbide levels in the coating.
The tungsten carbide WC-12Co coatings are resistant to sliding wear, impact, abrasion and fretting at temperatures up to 510°C (950 °F), preferably in non-corrosive media. We recommend chromium carbidecoatings for higher temperature applications.
Coatings that contain tungsten carbide protect substrates from the negative effects of fretting, abrasive grains, particle erosion and dynamic contact with hard surfaces.
These tungsten carbide coatings af steel can be used for abrasion-resistant coatings in dry, non-corrosive environments.
Although HVOF technology is frequently used for WC coating applications noticeable material oxidation and WC decomposition still occur during HVOF deposition.
The decomposition of WC-Co coatings is directly related to a high combustion temperature, usually more than 3,000oC (5,432°F), as well as the presence of oxygen in HVOF combustion products. This results in coating embrittlement and subsequent reduction of its service lifetime in conditions of abrasive and erosive wear.
Kermetico High-Velocity Air Fuel (HVAF) systems use gas fuel and compressed air for combustion at substantially lower temperatures and produce higher velocities than HVOF coating systems.
With the HVAF combustion temperature below 2,000oC (3,632°F), the surface temperature of Co-, Ni- and Fe-alloy particles usually remain near their melting point.
Depositing WC-Co coatings by the Kermetico HVAF spraying process eliminates WC coating embrittlement and improves its hardness and density.
It also reduces the production cost due to higher spray rates achieved and use of air instead of pure oxygen.
A distinguishing feature of the Kermetico HVAF process is that spray particles are heated but preferably not fused during spraying.
Kermetico HVAF WC-Co Coating Properties
| Feature | S.I. Units | U.S. Units |
|---|---|---|
| Apparent metallographic porosity | <0.1 | |
| bond strength of a tungsten carbide coating to carbon steel | 80+MPa @100 µm | 12,000+PSI @0.040” |
| hardness range, HV300 | 1,150-1,600+ | |
| hardness deviation from a target value, HV300 | ±6% | |
| typical as-sprayed roughness | 2-3.2 µm | 80-130 µinch |
| maximum working temperature of the coating | 510 oC | 950 oF |
Typical Applications Of HVAF WC-Co Coatings
Heavy Abrasive Wear and Erosion Resistance
- Steel rolls
- Corrugating rolls
- Agricultural rasp bars
- Exhaust fans
- Conveyor screws
- Sucker rod couplings
- Thread bars
Uniform high hardness and ductility, low stress and porosity lead to a substantial increase of service life of parts protected with Kermetico HVAF WC-Co coatings in comparison with HVOF tungsten carbide versions.